According to the International Data Corporation (IDC), 89% of businesses use cloud computing for at least part of their operations, reducing their IT cost by up to 40%. Before now, businesses expended energy managing and maintaining infrastructure on-site. Aside from being expensive, time-consuming, and unreliable, businesses find scaling difficult. However, companies’ and businesses’ IT problems can now be easily solved due to evolving technology, including cloud computing software.
It is crucial to note that switching cloud computing mediums for businesses can be a hard nut to crack, especially if the organization’s CEO needs more background knowledge of cloud computing services. Therefore, this article will explain the various cloud models, their differences, and how businesses can leverage them for high-level performance and high ROI.
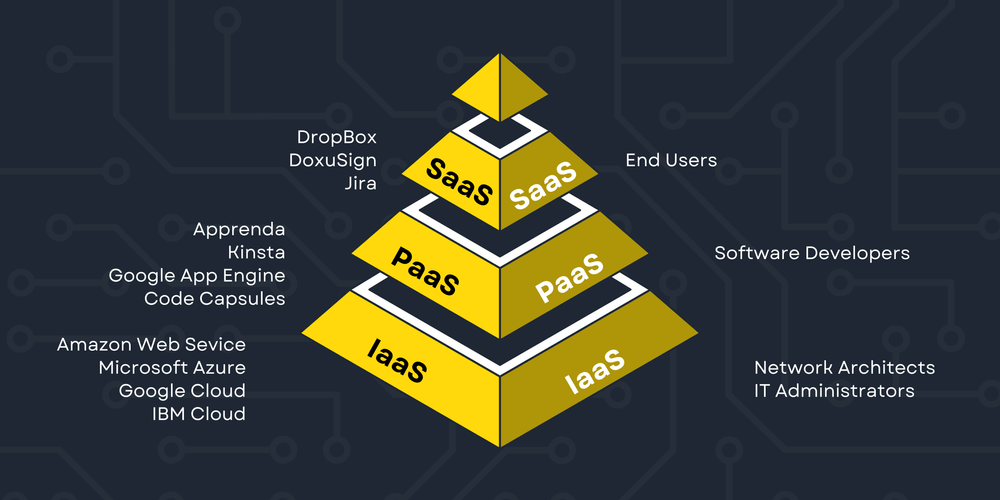
The 3 Types of Cloud Computing Services
SaaS
SaaS is the most common of all three cloud computing services. Many companies rely on SaaS products to run their projects because it is incredibly scalable, easy to use, and operate. SaaS employs the internet to deliver applications, which a third-party vendor manages.
Delivery
SaaS products depend on the internet to launch applications managed by a provider to the end users. Most SaaS platforms run on the web, so companies do not have to download and install this software on a central device before accessing it. Users can either utilize these products as a web app, for example, Google Docs, or download and install them on their devices, for example, Adobe Creative Cloud.
Furthermore, companies do not have to hire IT persons to manually install software on individual company computers with license keys—because of the easy use and accessibility of the SaaS product.
Common Examples of SaaS Solutions
Dropbox
Dropbox is a standard SaaS tool that allows multiple users within an organization to download, upload and share various files.
DocuSign
With this SaaS product, businesses can send files that require signatures to their clients.
Jira
Jira is a project management software. Businesses can access Jira based on a subscription.
Pros of SaaS
- Simple to use
- Doesn’t require an upgrade or users to manage the platform.
- Doesn’t use any space in the user’s storage, as Developers store everything in the cloud.
- Eliminates extra funding for SaaS Product maintenance.
- You can access it from anywhere.
Cons of SaaS
- Users do not have control of the cloud infrastructure the software runs on. So if there is a glitch from the vendor, it affects the users’ activities on the software.
- SaaS products can be incompatible with the standard tools of the user.
When to use SaaS
- Businesses or startups with little capital can leverage SaaS solutions to create applications or launch e-commerce stores.
- Large businesses also use SaaS tools for short-term projects.
- Businesses can also use SaaS products to manage short-term projects that need affordable, easy, and quick collaborations among team members.
- SaaS is excellent for applications that require both mobile and web access.
Limitations and Concerns of SaaS
- The user has no control over the software component; they hand over control to the vendor or service provider. However, the control is not limited to the SaaS software based on the appearance, version, or update but also the government and data. The product users may need to rework their governance and data security system to suit the functionality and features of the SaaS service.
- Cost is higher as the vendor manages the whole product.
- Cloud service providers may create a system that makes it easy for users to join a service, but is tough to opt out of.
- Data on a SaaS product is only partially secure. Developers may need to exchange Vast volumes of data to the backend data hubs of the SaaS tools. This exchange helps developers carry out essential software functionalities. Disseminating certain personal and company information to public-cloud-based SaaS services can cause the security of users to be compromised. Plus, it will cost users to move massive data workloads.
- Users may experience downtime and poor performance of SaaS tools. This compromise is because the producer manages and controls the SaaS service. Users rely on Cloud vendors to strengthen the service’s performance and security. Unplanned and planned maintenance, network problems, or cyber-attacks can affect the functioning of the SaaS tool despite suitable service-level agreement (SLA) protections in place.
PaaS
PaaS stands for Platform as a Service, one of the services carried out in cloud computing. They are cloud computing providers offering fully optimized web hosting services for deploying and developing cloud-enabled applications for business enterprises. PaaS software provides developers with a framework for building custom apps without bothering about how to serve, store, and manage data.
Delivery
PaaS offers ready-to-use programming components and infrastructure in the cloud for web developers and IT experts to build and manage web and mobile applications. It enables users to access the PaaS product through a platform or an online interface.
Common Examples of PaaS Solutions
Apprenda
With this PaaS product, developers and businesses can host the whole application portfolio and design and run different applications on this platform.
Kinsta
Kinsta provides various solutions, including a database, managed WordPress hosting solutions, and an application that allows organizations to deploy different web applications faster and easier without bothering about the hosting Infrastructure.
Google App Engine
Google App Engine allows developers to build and host web applications in cloud-based data centers that Google manages.
Code Capsules
Code Capsules is a cloud-based PaaS solution that delivers secure and fast deployment of the backend, frontend, and database instances. Code Capsules help companies get their applications to their target audience seamlessly.
Pros of PaaS
- It reduces cost. It provides an alternative for maintaining physical development infrastructure and IT staff.
- PaaS solution offers regular and automatic software updates, ensuring businesses are equipped with the latest trends and updates.
- Create room for flexible work hours. Developers can freely customize Applications without being tethered to a specific machine or workspace.
Cons of PaaS
- Security Risk. Users of PaaS products solely depend on vendors or third parties to protect their privacy. This means a poor security service can jeopardize any project.
- Users may need help with relying on tools outside the PaaS environment.
- PaaS product users have limitations on customizing or switching from one functionality to another.
- Developers can only control the app code and not the infrastructure it runs on.
- Users can access the developer’s information.
When to use PaaS
- Developers use PaaS products to create apps delivered via the web to the end-users as SaaS.
- PaaS enables different developers to work together on the same project.
- During collaborations, PaaS platforms facilitate workflow.
- PaaS allows flexibility and speed when users work on projects.
- PaaS is ideal for Developers seeking to build custom applications.
- Companies can use PaaS tools to reduce costs.
- PaaS tools streamline some difficulties that may arise if users rapidly deploy or develop an app.
Limitations and Concerns of PaaS
- Developers entirely depend on the vendor’s technical skills when using the platform.
- Users may get stuck in a program or interface they no longer use.
- Companies can use PaaS platforms to run their services and applications. But here’s the problem with these PaaS platforms. The data the third-party vendor controls and accesses in the cloud servers poses concerns and security risks. The user’s security alternatives may be restricted as they (the user) cannot use services with specific hosting systems.
- Developers may experience legacy system and customization problems. PaaS platforms may not be an ‘immediate and easy’ fix for existing legacy services and apps. Instead, developers may need different configurations and customizations for the legacy systems to function using the PaaS service. The final customization can lead to a complicated IT system. Which in turn can downplay the value of the PaaS investment.
- Developers may experience Runtime issues using the PaaS service. Apart from users facing limitations linked to specific services and apps, the PaaS platform may not be programmed for the frameworks and language the developer chooses. Also, some framework versions may perform less with the PaaS product.
- Developers may be unable to customize the cloud functioning using management automation workflows. This limitation is because the PaaS platform restricts the operational abilities of the developers. However, this system is aimed at reducing the functional responsibilities of users and losing active control may influence how developers provision, manage and operate.
IaaS
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing software that helps businesses organize and manage data as they thrive. They are on-demand cloud-enabled infrastructural resources organizations use to optimize their managerial and administrative activities. IaaS vendors manage customers’ data using physical servers globally.
Delivery
IaaS products virtually deliver servers, networks, storage, and systems to businesses. Companies can then access and manage data via a dashboard and connect it to the IaaS vendor’s Application.
Common Examples of IaaS
Amazon Web Service
Companies use this IaaS tool for on-demand cloud computing, and users can access it by recurring subscriptions. Amazon Web Service helps businesses store their data and produce content.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is a cloud-computing IaaS tool that helps organizations build, test, and manage applications using a network of Microsoft data hubs.
Google Cloud
Companies can use Google Cloud to run Oracle, Windows, and SAP. Also, companies can organize and manage their databases and utilize AI solutions to boost working efficiency.
IBM Cloud
With this IaaS product, organization members can allocate their network, storage, computer, and security resources on demand. This way, companies only utilize resources when needed, boosting the organization’s work efficiency.
Pros of IaaS
- Users only pay for what they need.
- Businesses have complete control of their infrastructure.
- It is easy to scale.
Cons of IaaS
- Users are responsible for the security of their data.
- Users manage data; if lost, only the user can recover it.
- The user is responsible for configuring the IaaS components.
When to use IaaS
- Companies use IaaS when they need to perform operational tasks; for example, application testing, high-performance computing, software development, web hosting, data analysis, etc.
- Startups and small businesses may prefer IaaS to prevent spending money and time creating and purchasing software and hardware.
- More prominent companies may prefer to control their infrastructure and applications completely, but they want to buy what they need.
- Businesses undergo fast growth like the scalability of IaaS, and they can change specific software and hardware-software effortlessly as their needs increase.
- IaaS’s product is ideal for companies that seek flexibility and scalability.
Limitations and Concerns of IaaS
- Switching from one IaaS vendor to another can be difficult.
- Users are prone to security threats. While SysAdmins control the middleware, apps, OS platform, and data, security threats can still come from other Virtual machines (VMs) or the host. System vulnerability or insider threat can disclose the data communication between the virtual machines and the host infrastructure to unauthorized sources.
- Due to the complexities of the IaaS product, companies may have to organize further training and resources. This training is to help the company’s workforce learn how to run the system infrastructure properly. Users will be tasked with securing data, backing up data, and business continuity. Because of the incomplete control of the infrastructure, managing and overseeing may be challenging without prior training and resources.
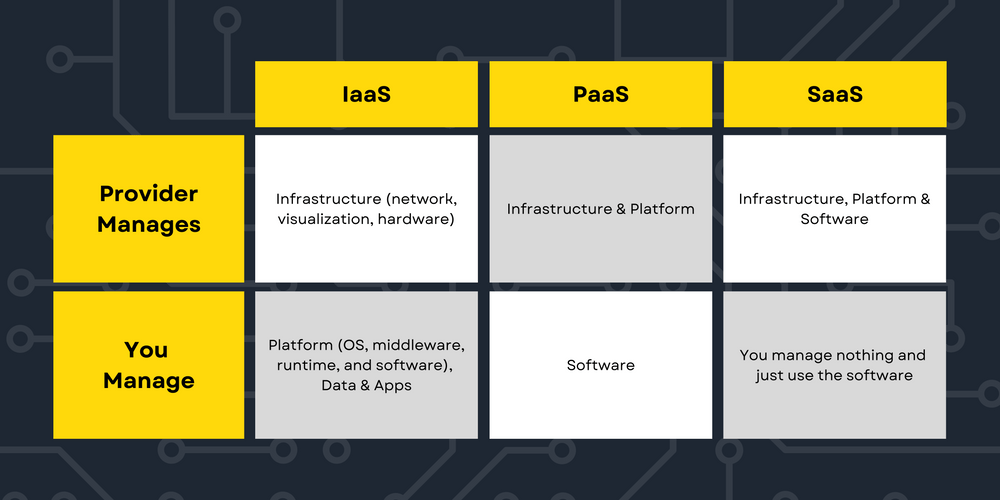
IaaS vs. PaaS vs. SaaS: Key Differences
The critical difference between SaaS PaaS and IaaS is the user’s level of control and responsibility while using the software. For example, the vendor sets the SaaS Project framework, leaving no room for customization. PaaS allows users to customize the components while the provider manages the software and infrastructure. And in IaaS, users can fully customize the features while the vendor manages the infrastructure.
Conclusion
Cloud computing models are easy to use, convenient, and ideal for storage. Businesses can now use cloud-based products to manage infrastructures, access tools, and create apps without a physical server— increasing efficiency, productivity, and result.
