The MERN stack, which stands for MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js, is a robust framework for web application development. To ensure that MERN applications are agile and responsive, it’s essential to focus on performance optimization. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into actionable insights to enhance performance.
Efficient Database Operations with MongoDB
a. Use Indexing Strategically
What is it? Indexing in MongoDB is a key strategy to boost query performance. Without appropriate indexing, MongoDB would need to scan every document, which can be highly inefficient, especially for large datasets.
Tip: Create indexes using:
db.collection.createIndex({ fieldName: 1 });
However, be cautious about over-indexing, as it can slow down write operations. You can monitor query performance with:
db.collection.find(query).explain("executionStats");
b. Opt for Projection
Fetching only the necessary data accelerates queries and reduces network overhead.
Example: To retrieve just the `name` field from a collection:
db.collection.find({}, { name: 1, _id: 0 });
c. Avoid Blocking the Event Loop
Mongoose’s model instances come with overhead. For faster operations, retrieve plain JavaScript objects.
Tip: Use:
Model.find().lean().exec();
Streamline Your Express.js App
a. Use Gzip Compression
Compressing API responses significantly reduces data transfer times.
Implementation: After installing the `compression` middleware:
const compression = require('compression');
app.use(compression());
b. Cache Middleware
Implementing caching for frequently accessed routes can decrease server load and improve response times.
Tip: Implement `apicache`:
const apicache = require('apicache');
const cache = apicache.middleware;
app.get('/your-route', cache('5 minutes'), (req, res) => ... );
Boost React Performance
a. Virtualize Long Lists
Efficiently render long lists using libraries like `react-virtualized`, which only display visible items.
Example: Using the `List` component from `react-virtualized`:
import { List } from 'react-virtualized';
b. Immutable Data Structures
Utilize `immutable.js` to prevent unintended data changes, optimizing React’s rendering process.
Example: Using Immutable List:
import { List } from 'immutable';
const myList = List([1, 2, 3]);
c. Code Splitting with React Lazy and Suspense
Divide your app into smaller bundles, loading only what’s necessary.
Implementation:
const MyComponent = React.lazy(() => import('./MyComponent'));
...
<React.Suspense fallback=<div>Loading...</div>>
Optimize Node.js Server Performance
a. Asynchronous Code
Embrace JavaScript’s async features to prevent blocking the main thread.
Example: Using async/await for database calls:
app.get('/data', async (req, res) => {
const data = await db.fetchData();
res.send(data);
});
b. Profiling and Monitoring
Regular monitoring helps identify potential bottlenecks.
Tip: Use `node –inspect` to debug and profile your app, visualizing results in Chrome’s DevTools.
c. Clustering
Utilize multi-core systems by running multiple Node.js instances.
Example: Using Node’s `cluster` module:
const cluster = require('cluster');
const numCPUs = require('os').cpus().length;
if (cluster.isMaster) {
for (let i = 0; i < numCPUs; i++) {
cluster.fork();
}
} else {
require('./server');
}
Networking and API Calls
a. Efficient Data Fetching
Enhance user experience and efficiency by fetching only necessary data.
Tip: Implement infinite scrolling in React using libraries like `react-infinite-scroll-component`.
b. Use Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
CDNs like Cloudflare or AWS CloudFront serve content from a location nearest to the user, reducing load times.
DevOps Practices for Performance
a. Minification and Bundling
Optimize JavaScript by bundling and minifying it using Webpack.
Example: In your `webpack.config.js`:
module.exports = {
...
mode: 'production'
};
b. Continuous Monitoring
Monitor real-time performance metrics to detect and address issues promptly.
Tip: Platforms like New Relic or Datadog provide invaluable insights and alerts for inefficiencies or issues.
Enhancing App Performance with Code Capsules in MERN Stack
Optimizing Your Code Capsules Profile for MERN Stack
Initiate your journey by establishing a Code Capsules account, specifically tailored for MERN stack optimization. Carefully complete your profile setup, ensuring it aligns with performance enhancement strategies for MERN applications.
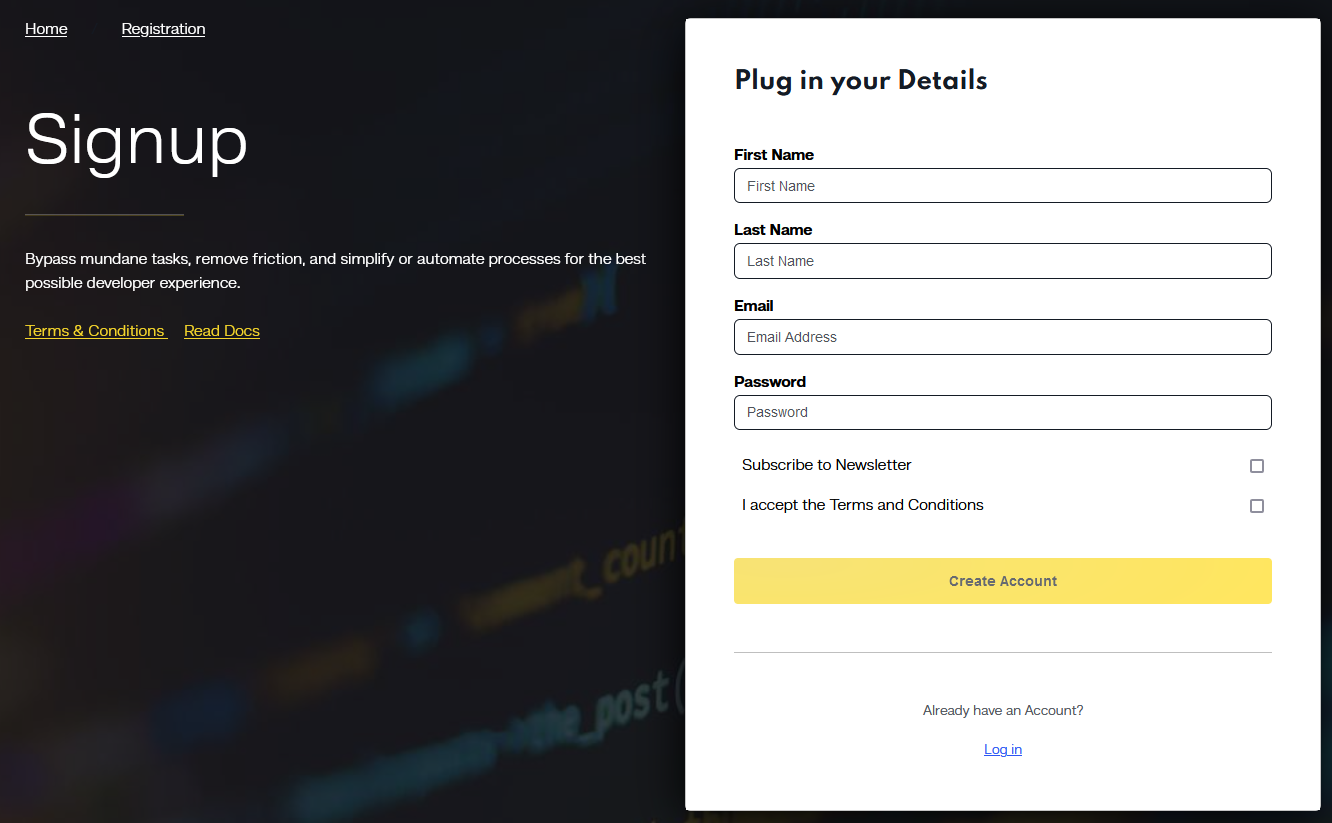
Streamlining MERN Project Management in Code Capsules
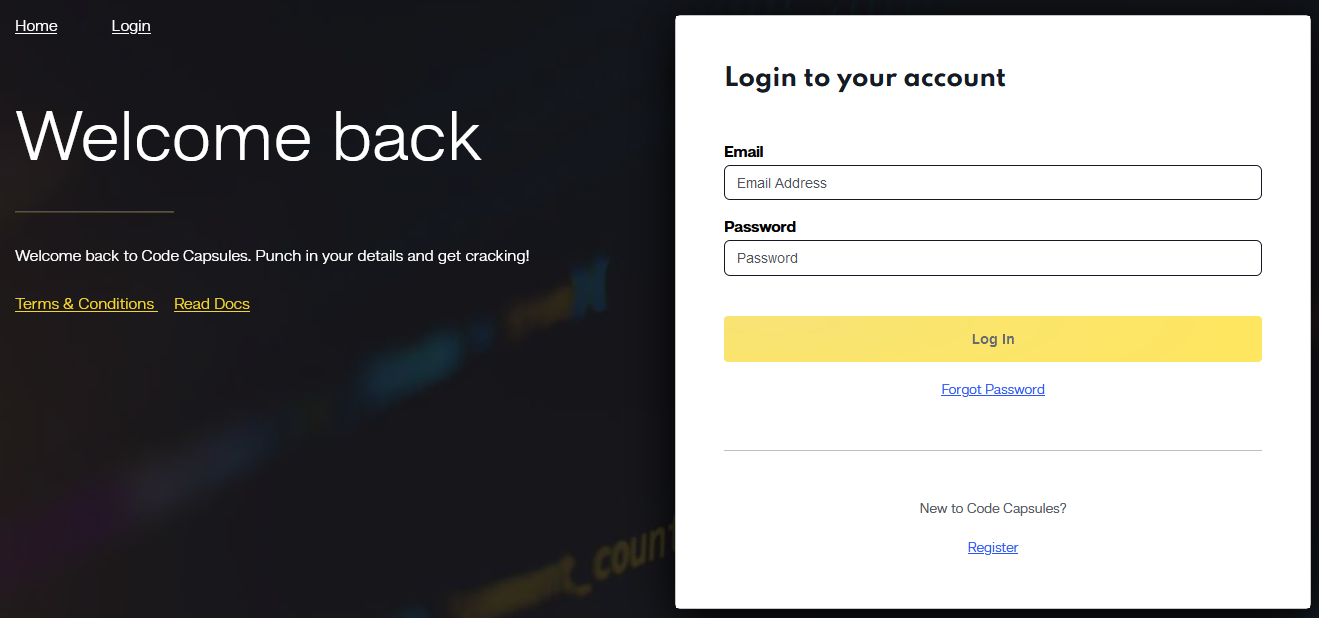
Post-registration, access your Code Capsules dashboard to manage MERN stack projects. This space is optimized for performance tracking and efficient deployment of MERN applications.
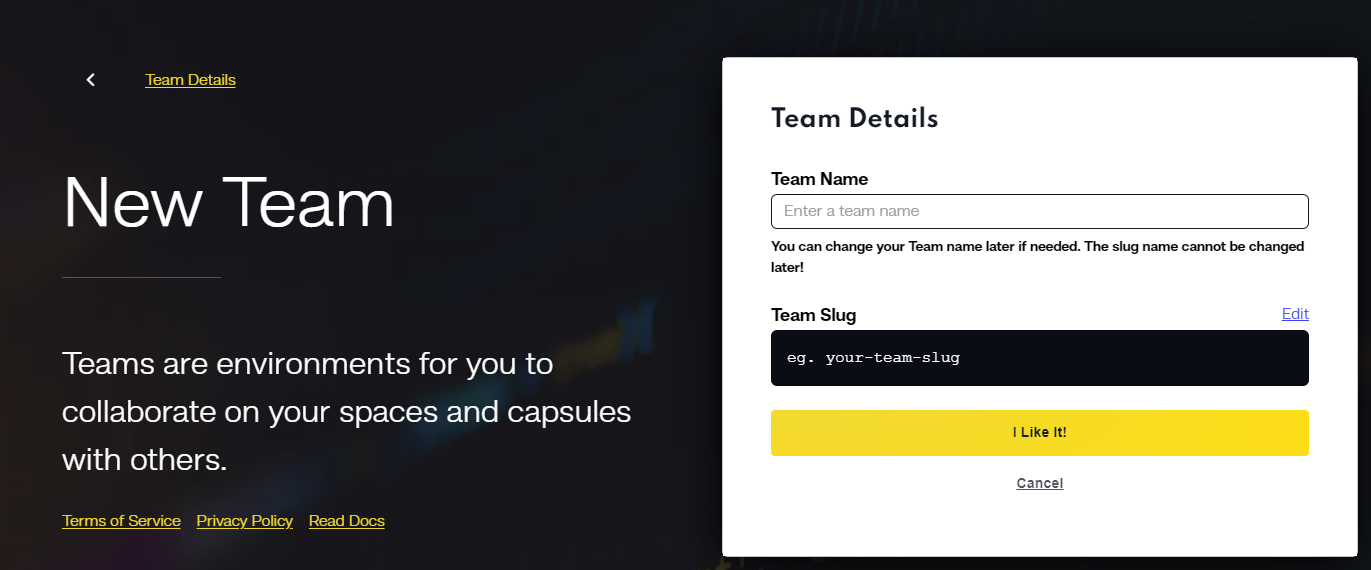
Formulating a High-Performance MERN Team in Code Capsules
In Code Capsules, establish a team that specializes in MERN stack optimization. This step is crucial for collaboratively enhancing application performance and handling complex MERN projects.
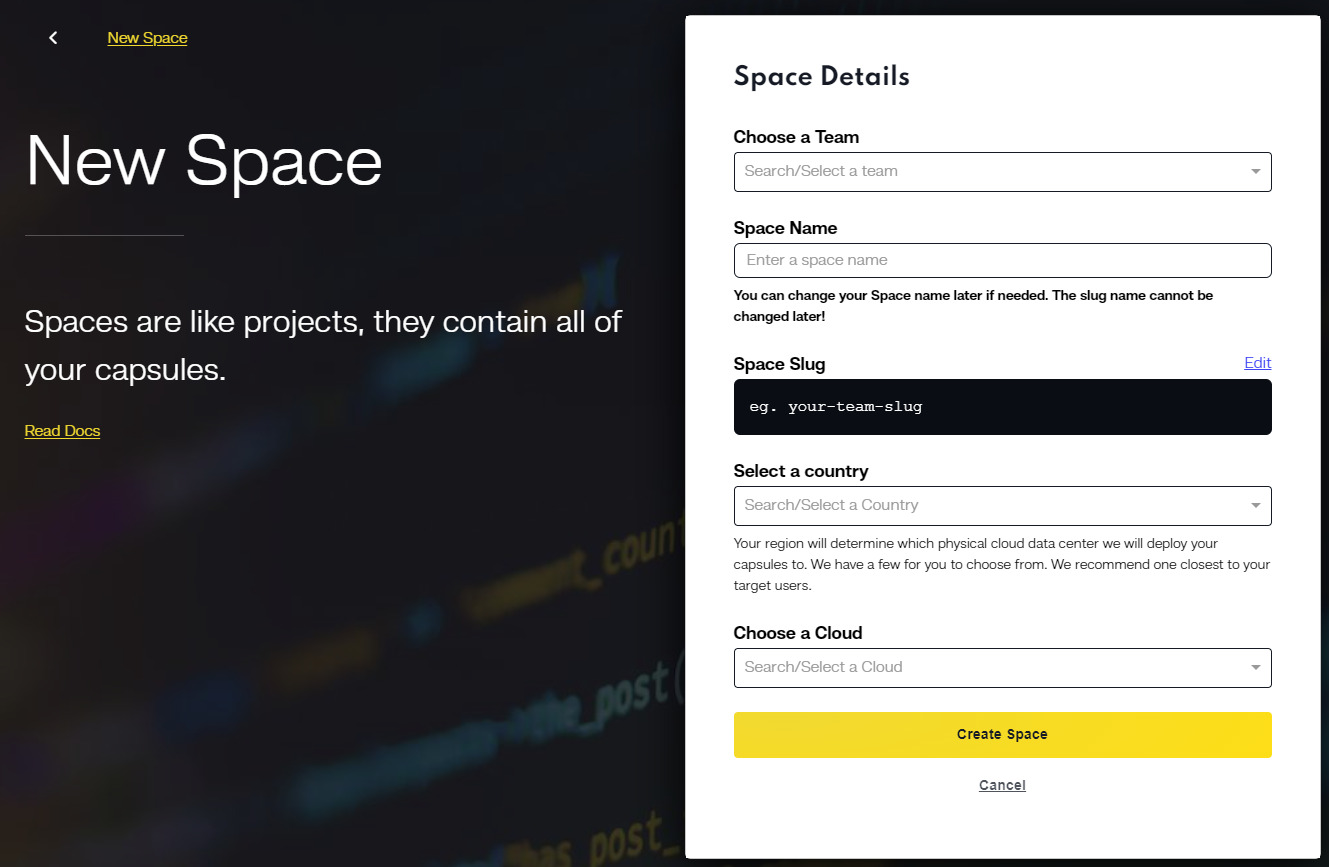
Setting Up Performance-Optimized Spaces for MERN in Code Capsules
Within Code Capsules, create spaces dedicated to MERN stack projects. These spaces are designed to host and run your applications in environments that are fine-tuned for maximum performance.
Launching Performance-Focused Capsules for MERN
Start a new capsule in your MERN-optimized space, conceptualizing these as individual project units. These capsules are configured to enhance the performance of each component of your MERN application, such as the front-end, back-end, or server configurations.
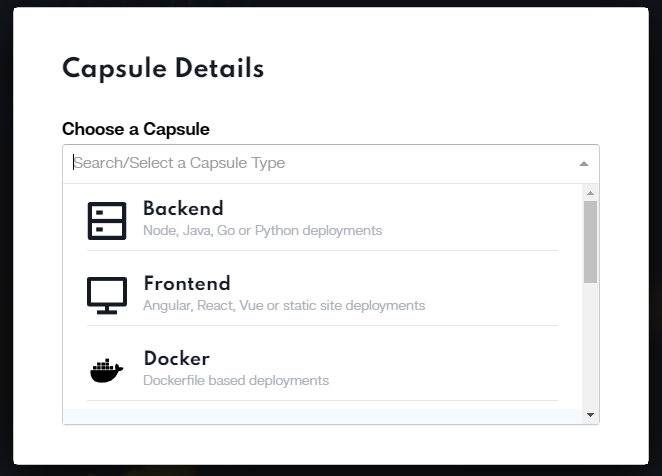
By following these modified steps focused on MERN stack performance, you can efficiently deploy and manage your applications on Code Capsules, leveraging the platform’s capability for optimized MERN application performance and deployment.
Conclusion
Perfecting performance in a MERN stack application isn’t a one-time task but a continuous process of assessment and refinement. With the right strategies, tools, and a commitment to excellence, developers can deliver blazing-fast, highly responsive applications that excel in real-world scenarios. Always remember, in the realm of web applications, speed and responsiveness aren’t just features—they’re necessities.